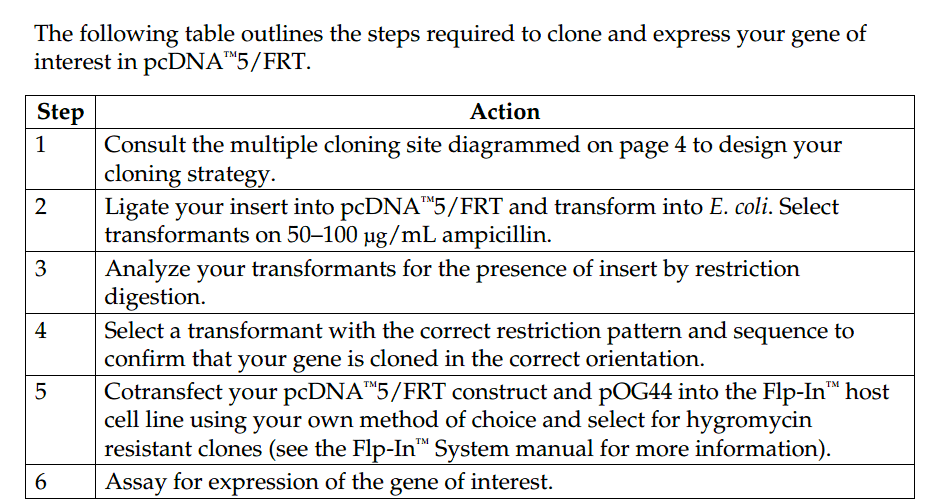
pcDNA5-FRT vector is a 5.1 kb expression vector designed for use with the Flp-In System. This vector features: 1. CMV promoter for high level expression in mammalian cells; 2. ten unique restriction site for easy cloning; 3. FLP Recombination Target (FRT) site for Flp recombinase-mediated integration of the vector into the Flp-In host cell line and 4. Hygromycin resistance gene for selection of
stable cell lines.When cotransfected with the pOG44 Flp recombinase expression plasmid into a Flp-In mammalian host cell line, the pcDNA5/FRT vector containing the gene of interest is integrated in a Flp recombinase-dependent manner into the genome. pcDNA5/FRT 载体含有以下元件: The human cytomegalovirus (CMV) immediate-early enhancer/promoter for high-level constitutive expression of the gene of interest in a
wide range of mammalian cells (Andersson et al., 1989; Boshart et al., 1985; Nelson et al., 1987)
Multiple cloning site with 10 unique restriction sites to facilitate cloning the gene of interest
FLP Recombination Target (FRT) site for Flp recombinase-mediated integration of the vector into the Flp-In host cell line
Hygromycin resistance gene for selection of stable cell lines (Gritz & Davies,1983)
The control plasmid, pcDNA5/FRT/CAT, is included for use as a positive control for transfection and expression in the Flp-In host cell line of choice.
For more information about the Flp-In System, the pOG44 plasmid, and generation of the Flp-In host cell line, refer to the Flp-In System manual. The Flp-In System manual is supplied with the Flp-In Complete or Core Systems 关于pcDNA5/FRT 载体的注意事项 The pcDNA5/FRT vector contains a single FRT site immediately upstream of the hygromycin resistance gene for Flp recombinase-mediated integration and selection of the pcDNA5/FRT plasmid following cotransfection of the vector(with pOG44) into Flp-In mammalian host cells. The FRT site serves as both the recognition and cleavage site for the Flp recombinase and allows recombination to occur immediately adjacent to the hygromycin resistance gene. The Flp recombinase is expressed from the pOG44 plasmid. For more information about the FRT site and recombination, see the next page. For more information about pOG44, refer to the Flp-In System manual. The hygromycin resistance gene in pcDNA5/FRT lacks a promoter and an ATG initiation codon; therefore, transfection of the pcDNA5/FRT plasmid alone into mammalian host cells will not confer hygromycin resistance to the cells. The SV40 promoter and ATG initiation codon required for expression of the hygromycin resistance gene are integrated into the genome (in the Flp-In host cell line) and are only brought into the correct proximity and frame with the hygromycin resistance gene through Flp recombinase-mediated integration of pcDNA5/FRT at the FRT site. For more information about the generation of the Flp-In host cell line and details of the Flp-In System, refer to the Flp-In System manual. Flp重组酶介导的DNA定向重组 In the Flp-In System, integration of your pcDNA5/FRT expression construct into the genome occurs via Flp recombinase-mediated intermolecular DNA recombination. The hallmarks of Flp-mediated recombination are listed below.
Recombination occurs between specific FRT sites on the interacting DNA molecules.
Recombination is conservative and requires no DNA synthesis; the FRT sites are preserved following recombination and there is minimal opportunity for introduction of mutations at the recombination site.
Strand exchange requires only the small 34 bp minimal FRT site .
For more information about the Flp recombinase and conservative site-specific recombination, refer to published reviews (Craig, 1988; Sauer, 1994). FRT位点 The FRT site, originally isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, serves as a binding site for Flp recombinase and has been well-characterized (Gronostajski & Sadowski, 1985; Jayaram, 1985; Sauer, 1994; Senecoff et al., 1985). The minimal FRT site consists of a 34 bp sequence containing two 13 bp imperfect inverted repeats separated by an 8 bp spacer that includes an Xba I restriction site. An additional 13 bp repeat is found in most FRT sites, but is not required for cleavage (Andrews et al., 1985). While Flp recombinase binds to all three of the 13 bp repeats, strand cleavage actually occurs at the boundaries of the 8 bp spacer region (Andrews et al., 1985; Senecoff et al., 1985).